Section: New Results
Internet of Things (IoT) and Information Centric Networking (ICN)
Low-power Internet of Things with NDN and Cooperative Caching
-
Participants: Oliver Hahm, Emmanuel Baccelli, Thomas C. Schmidt, Matthias Wählisch, Cédric Adjih, and Laurent Massoulié
Energy efficiency is a major driving factor in the Internet of Things (IoT). In this context, an IoT approach based on Information-Centric Networking (ICN) offers prospects for low energy consumption. Indeed, ICN can provide local in-network content caching so that relevant IoT content remains available at any time while devices are in deep-sleep mode most of the time. In our paper on the subject, we evaluated NDN enhanced with CoCa, a simple side protocol we designed to exploit content names together with smart interplay between cooperative caching and power-save sleep capabilities on IoT devices. We performed extensive, large scale experiments on real hardware with IoT networks comprising of up to 240 nodes, and on an emulator with up to 1000 nodes. We have shown in practice that, with NDN+CoCa, devices can reduce energy consumption by an order of magnitude while maintaining recent IoT content availability above 90 %. We furthermore provided auto-configuration mechanisms enabling practical ICN deployments on IoT networks of arbitrary size with NDN+CoCa. With such mechanisms, each device could autonomously configure names and auto-tune parameters to reduce energy consumption as demonstrated in our paper.
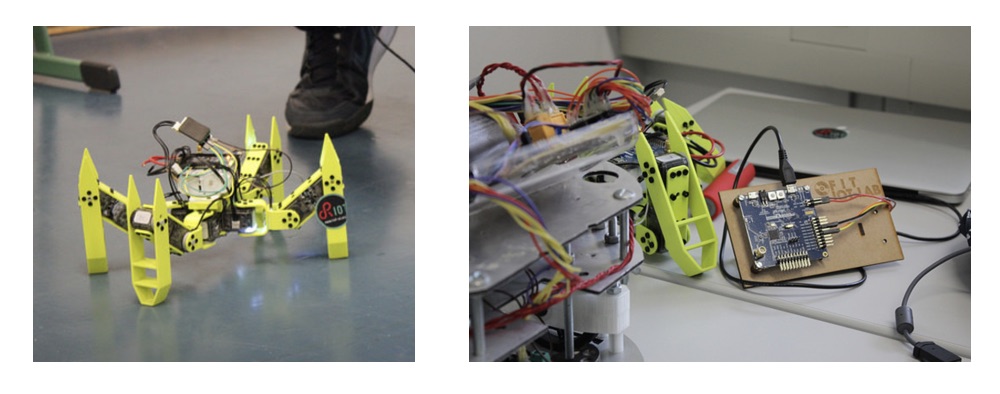
Information Centric Networking for the IoT Robotics
In the near-future, humans will interact with swarms of low-cost, interconnected robots. Such robots will hence integrate the Internet of Things, and coin the term IoT robotics. Using ROS (Robot Operating System) is currently the dominant approach to implement distributed robotic software modules communicating with one another. ROS nodes can publish or subscribe to topics, which are named and typed data streams sent over the network. In our work on the subject, we presented preliminary work exploring the potential of using NDN as network primitive for ROS2 nodes (the newest version of ROS).
Data Synchronization through Information Centric Networking
The use of Named Data Networking (NDN) for distributed multiuser applications, e.g. group messaging and file sharing, requires NDN synchronization protocols to maintain the same shared dataset (and its updates) among all nodes. ChronoSync, RoundSync, and PartialSync are some proposals to address this issue.
In our work on the subject, we focused on the state-of-the-art protocol RoundSync: we study its core features, that permit participating nodes to detect, propagate, and reconcile all changes. Particular attention is given to the case of multiple changes per round. We then proposed an improved variant, iRoundSync, that exchanges fewer messages in the multiple-change case and is more resilient to packet losses. We have quantified the performance gain of iRoundSync on a simple topology.